How Did Language and Art Influence the Stine Age
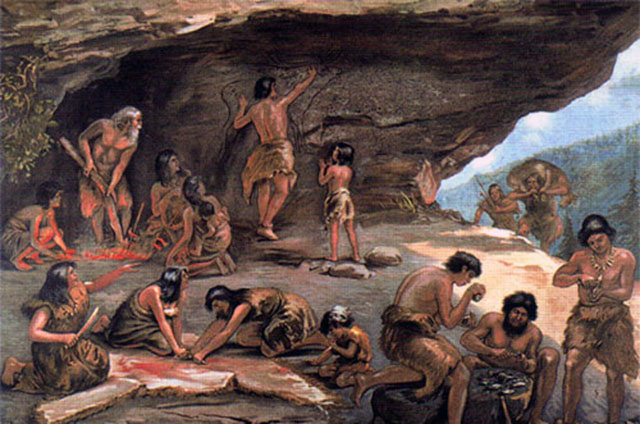

A development of the man spirit, especially in the Center Paleolithic, contributed to the emergence of speech and language, art, religion and technical skill. Speech over time went through the post-obit development path: the first stage is characterized by general pantomime accompanied by additional stuttering, in the second stage paleolithic people started to communicate with precise gestures associated with corresponding voice symbols or words and at the end in the third stage pantomime and stuttering completely disappeared. People started to use systematic signs and words. At the beginning of the third phase appeared analytical thinking and terminal. Since that time, talking and thinking, recorded a abiding rise..

The voice communication, in the beginning, was unarticulated. Humans in old stone age used unrelated cries to limited their joy, hurting, sadness, happiness, hatred, fearfulness, etc. Later, when they made sense to an every sound, man has passed on to then called articulated speech. Along with the speech and language paleolithic people evolved. Linguistic communication has become a tool of thought. Its part was to found communication between people in club to exchange their knowledge and experiences. When language appeared, it initiated the need of people to tell something to i some other. Complex and various situation, over time, more and more enriched language. Thanks to the language all their knowledge passed on to their descendants. Language and spoken language greatly helped, and facilitated their engagement on the creation of improve living conditions. Without information technology, people certainly would not take been able to achieve all that humanity has achieved today.
Closely associated with stance, language has gone through a long development mode from unarticulated – sound all the manner to articulated gender and tribal languages. Later, with the appearance of grade societies, tribal linguistic communication was suppressed, and instead of it appeared languages of nationalities or nations. At the end of the Stone Age and the beginning of the Iron Age there have been established following linguistic groups:
- Indo-European, consisting of Indian, Iranian, Romanian, Slavic, Germanic and Celtic languages;
- Tartar-Mongolian, which includes languages of tribes and nationalities of Central Asia, Tatar and Mongolian;
- Chinese-Tibetan, which includes languages of an E Asia, China, Tibet, Vietnam and Burma;
- Hamito-Semitic, which includes languages of northern and fundamental Africa and Arabia,
- Finnish-Hungarian includes Hungarians, Finns, Estonians and others less familiar.
In the Paleolithic era, an art was born as another of import cistron of social and spiritual knowledge of the paleolithic people. Development of the art was initiated past the human being's need to express its relationship with nature and economy, i.e. to present its daily life through images. Paleolithic people, which lived in Upper Paleolithic, by spending free energy on food collecting and hunting and by fighting with raw nature simultaneously, began to develop, and raise art high above their pocket-sized possibilities. The initial manifestations of fine fine art, dates dorsum from the Mousterian culture. First creative work was found in the La Fère , in France and in the cave, in Georgia. Those were usually dents in the shape of a glass, perfectly arranged on the stone plate, then bone with parallel stripes, also ochre fingerprints and in the end pieces of stone carved with straight lines.

Most valuable works of art made paleolithic people of Aurignacian and Magdalenian culture. These people not merely did they decorated small items but they busy likewise walls of caves particularly in southern France and northern Spain.
The nearly paleolithic artistic cases is so-called "Venus", i.e. statuettes of women, unremarkably naked with highly highlighted markings of the sex activity, while other parts of the body are completely ignored. This is explained with the important role of women in the society at the time. At the same time, in male statuettes, which are rarer than women, male characteristics are pointed out. Numerous statuettes accept been plant in the wider surface area of the Pyrenees Peninsula all the manner to Lake Baikal. Amidst the virtually of import sites are caves Brassempouy in France, settlement Willendorf in Austria, Grimaldi caves in Italy, the settlement Gagarino and Kostyonki in Russia and and so on.
Paleolithic art
Painting of the Centre Paleolithic is more related to animals than to people, which is sufficient indication that hunter'due south way of life was very much present at the time. Among other things, paleolithic people painted mammoth, rhinoceros, deport, bison, bull, deer, horses and other animals. This was usually done on cavern walls in white, yellow and black colour and in the life-size. The human being characters are mostly presented in statues that were made of tusk or mammoth basic, soft stones, and sometimes of ash mass, drawings were rare.
Older examples of cave paintings have been establish in Western Europe in the territory of Spain, in the cavern of Altamira, then in French republic, in the cave Lascaux and after in Russia, in a cave Kapovaya in the Urals.
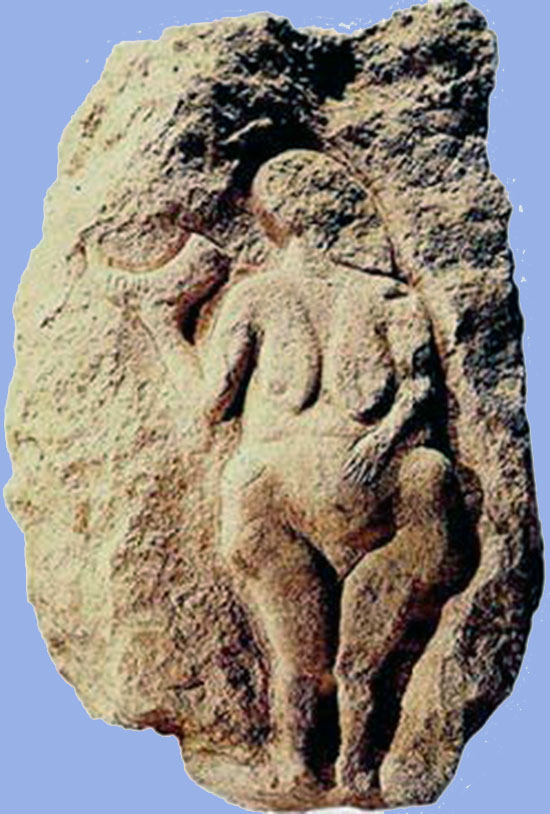

Artists of Aurignacian culture, among other things, used ornamental elements showing the beginnings of stylization. That is how some of their "Venus" has already been stylized. The most common monuments of dwelling arts are tiny drilled and carved profiles of beast heads that were probably worn as an amulet, as well busy lamps and palettes that look like fishes and things like that.
It is interesting that many of the most famous caves are very deep and caves passages are winding, so it is very hard to reach places where art of work was drawn, because of the dangerous abyss and waterfalls, and narrow passages and cracks in the rocks. Paleolithic artists beginning had to find a identify to paint so-called gallery, then they had to force out the cave lion and bear, and when all this things were done artists could start their piece of work. They performed work of fine art with very trivial light that torches could provide and lamps purged with grease or fat. They tireless and deliberately sought, and ultimately found a rock inside a cave which had to be far abroad from familiar exterior world and life the rocky wall had to be far abroad from everything that was happening in the cave entrance.
Paleolithic artists were determined to paint animal images deep in the Earth's womb. And then many of them had to clamber to get to the identify of painting, or they had to wriggle and climb through very narrow gaps between the rocks. The artists, who painted very high on the cave rocks, could only do so by standing on the shoulders of ane of his companions. To reach, for example, the interior of the cave Montespan, i.east. the place where a bear figure was discovered, first they had to cross an underground river, which was followed by three hours walk and severe physical stress. All the fashion to the cavern gallery leads a passage, well-nigh 720 meters long with walls that are quite handy for painting or carving, but these walls were not interesting for Paleolithic artists.

Paleolithic art is closely continued with religion. Particularly it was used so-called magic incantations, whose purpose was to ensure a successful chase and to increase the power of life. In this regard, various magical means were made such as spear throwers with the carved figures of deer, mammoth and ibex, and so pallets in the shape of fish or horse heads, etc. Paleolithic art, compared to, artistic cosmos of Mesolithic era is characterized by great realism.
Paleolithic songs and dances
An important characteristic of Paleolithic fine art was made up of songs and dances. It is even possible that people started to dance before the Upper Palaeolithic, just it is assumed that they knew to sing and recite. At that time in that location were so-called ritual dances and poetic art that formed the epic story, genealogy of ancestors and some other works. The original song was equanimous by rhythmic speech.
Dance was directly related to singing and playing instruments.
Religion in Sometime stone age
A very important form of social consciousness is religion. Information technology reflects interpersonal relationships, variety of human activities every bit well as a set of opinions that were related with believing in the existence of supernatural forces. A religion occurs due to the man inability to explain the properties of some living things, objects and natural phenomena. Information technology appeared a long time agone based on mysterious and naive people's performances about their personal and external nature. In addition, religion appeared based on human inability to fight with nature, which is primarily driven by the depression level of economic activity.
Death is an inexhaustible source from which religion is constantly drawing its incentives. Magic based all its piece of work on decease as well. The idea that the spirit of man could continue to live, but reborn in another body, has a very long history. At the same fourth dimension, information technology was born an awareness of the afterlife. The marvel of the man listen is expressed through human being's desire to explicate the world. Man became more and more aware and that sensation has led him to learn many things about nature, guild and culture. This noesis paleolithic person put into their myths in which ghosts and devines of different shape and sizes played the almost important role.
Paleolithic burial
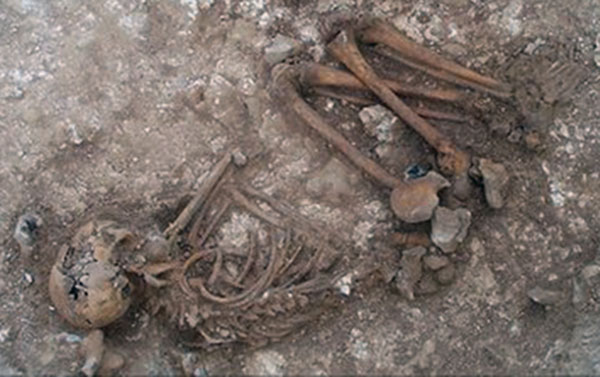
The primeval religious shows are related to the Neanderthal men, for whom it is believed to have beginning started to coffin their dead. Funerals were done inside the cavern, where they lived. They placed expressionless man in small-scale awfully dug hollows in the pose of a man lying on his side, with his knees slightly aptitude. The body of the deceased was buried with dearth, stones or stone plates.
In the tombs, next to a dead body information technology was discovered pieces of meat, flint and tools fabricated of bones besides as ruby colour, which symbolized claret, that is the source of new life. All these are evidences that it was present some form of conventionalities in the afterlife or existence in the life after death.
At the end of Upper Paleolithic deceased were, when it comes to the body position, buried from one occasion to some other. There was non some specific position characterized for that period. Some deceased were placed on their hip, while some deceased had their legs stretched in straight position, and some were lying on their back, and were often there were those who lay on their hips with their knees placed up to the mentum.
Totemism
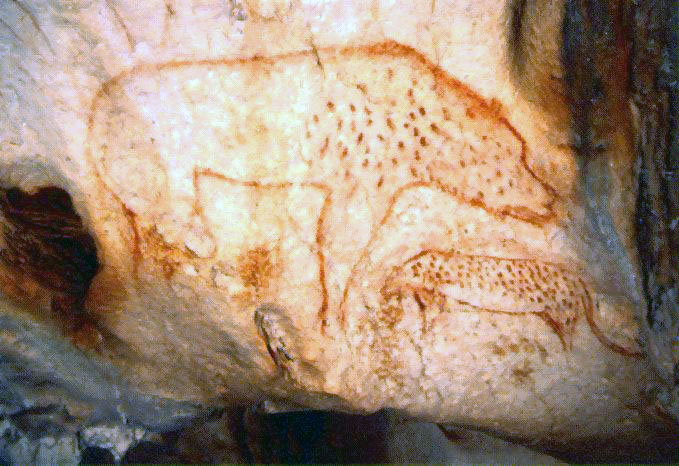
For hunting peoples of the belatedly Paleolithic period, the oldest form of religion is linked to these people. Among the beginning religions was totemism (totem – their gender) i.e. a belief in relationship between group of people and animals, plants and fishes. Paleolithic people believed that among animals and plants there are same relation equally it was among people. They also believed that some animals have a mutual ancestor with members of a particular race. That beast or plant has become their totem, their protector. That is the reason why some tribes bear the name of their totem, which were for example: "dragon", "wolf", "hawk" and and then on. Members of the tribe or gender could non kill an creature or damage a plant that they considered their totem, their antecedent and protector. This is so – called taboo arrangement or prohibition, which, at the same, was related to the prohibition of marriage inside the same totemic groups. The remains of totemism are present nevertheless today in the earth, especially in Australia, Malaysia, and in N American Indians.
Animism in Paleolithic age
At the same time, with totemism came new – another form of religion known as animism (lat. counterinsurgency – spirit, soul). Information technology is a term for the belief that all living things, fifty-fifty things accept a soul. The souls of the dead ancestors are settled in the living and non-living objects of the nature, as a not-corporeal spirits who possess supernatural powers. Over fourth dimension, they created shows about an individual soul and its moving in to another earth. Co-ordinate to this belief, death is simply the cessation of physical, just not of spiritual life. The soul remains to live.
Paleolithic humans constantly encountered the unknown and unclear appearances. Nevertheless, they contributed all of that to the power of spirits, because they wanted to live in peace, harmony and love with them. Paleolithic humans did not forget about their spirits non fifty-fifty when eating. They prepared nutrient for spirit in special dishes, assertive that their appetites are the aforementioned or like to humans. Nutrient that was left for the spirits humans chosen the victim, while sacrifice that was giving to spirits was called a sacrifice. In the beginning, people offered to spirits cede in the course of everything what they had to eat. There were evil and skilful spirits to whom paleolithic people regularly prayed and kept away.
Humans did not equally care for all spirits. They were afraid of some spirits while for other spirits they believed to exist good and friendly towards them. Animism was precursor of the belief in the afterlife and the cult of ancestors, i.e. a conventionalities which was based on the understanding that the spirit of an ancestor continues to live after death. The body of the deceased was covered in shells, sprayed with ruby colour equally a symbol of blood and burn. Cults of nature came to the scene with evolution of agriculture and livestock breeding. People in Stone age felt a very stiff fear of nature, and at the aforementioned time they felt an urge and desire to appease the nature. Due to this, people began to worship the dominicus, earth, burn, water and then on.
Fetishism
Afterwards in relation to the totemism and animism came to the scene fetishism as another form of religious consciousness. Fetishism was based on a belief in the supernatural power of some objects. Archaic people worshiped diverse different objects or they carried those objects with themselves believing that it will salve them of all evil and misfortune.
Paleolithic people, as well aforementioned religious agreement, also dealt with magic. They performed certain formalism actions with the goal of acting on supernatural powers, fulfilling their wishes. According to that, magic had a great touch on the unabridged life of humans in stone age. The all-time evidence for this are numerous drawings of animals pierced with spears, arrows, harpoons and the like, which all together, according to the belief of paleolithic people, should touch on on more happier and successful hunt. Magical operations were performed for at least 2 reasons. The first reason was to achieve certain textile or spiritual gain, and the other reason was done with the aim of harming opponents. In the organized religion of some archaic tribes and people, magic is present even today.
After, during collapsing of gender society, a cult of water was adult which together with a cult of different natural disasters with time evolved into the cult of the gods.
Salvage
frenchpallarcups1958.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.shorthistory.org/prehistory/language-and-spiritual-culture-in-old-stone-age/
0 Response to "How Did Language and Art Influence the Stine Age"
Post a Comment